Atom Bomb
The principle of fission is made use
of in the construction of the atom bomb. As atom bomb consists essentially of
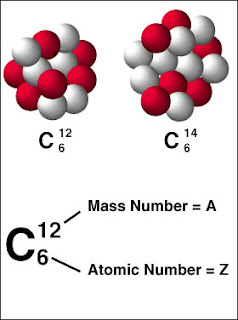
two pieces of 92U235 (or 92Pu239)
each smaller than the critical size and a source of neutrons. The subcritical
masses of U235 in the form of hemispheres are kept apart by using a
separator aperture (Fig 1).
Fig 1
When the bomb has to be exploded. A third well fitting cylinder of U235 ( whose mass is also less then
critical mass) is propelled so that it will fit in or fuse together with the
other two pieces. Now the total quantity of U235 is greater than the
critical mass. Hence an uncontrolled chain reaction takes place resulting in a
terrific explosion.
The explosion of an atom bomb releases tremendously large quantity of energy
in the form of heat, light and radiation. A temperature of millions of degrees
and a pressure of millions of atmospheres are produced. Such explosions produce
shock wave, They are every dangerous because the waves spread radioactivity in
air and cause loss of life.
The release of dangerously radio active γ-rays,
neutrons and radioactive materials presents a health hazard over the
surroundings for a long time.
The radioactive fragments and isotopes formed out
of explosion adhere to dust particles thrown into space and fall back to earth
causing a radiation “fall-out”, even at very distant places.